Recession or not, expect slower growth in spending is inevitable
main text
Recession or not, expect slower growth in spending is inevitable

While there may still be many plastics processors that continue to experience bottlenecks in the supply chain, a growing number of manufacturers now find themselves struggling with just the opposite problem — oversupply and lagging demand.
Global supply chains have steadily improved in recent months, and this is especially true in the U.S., where in certain market sectors, supply chains are functioning at or near their pre-pandemic levels. Unfortunately, some of the improvement in the supply chain situation is due to the fact that consumer demand for many types of goods is now steadily slowing.
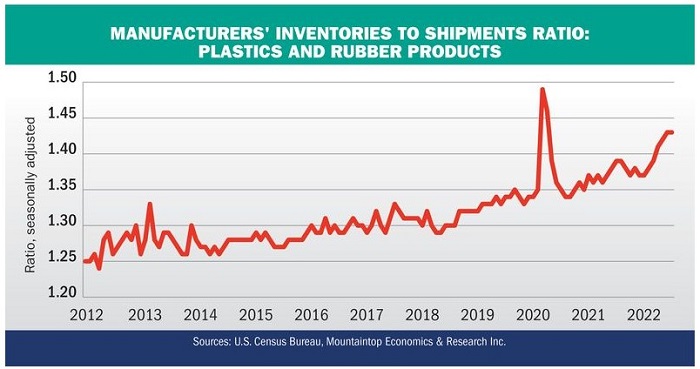
The chart indicates the overall levels of inventories in the plastic and rubber products industries are well above trend at the present time. I am not yet too alarmed by this because there are mitigating circumstances for why this might be the case. Nevertheless, it behooves us all to be wary of the risks and the volatility in the current economic environment.
Exacerbating the problems associated with varying imbalances in the forces of supply and demand are the issues stemming from the recent sharp rise in interest rates and the spiking volatility in foreign exchange markets. The result is a situation in which deft inventory management is not only increasingly crucial to the health of your company but also more uncertain and riskier than ever before.
Hear more from Bill on our Numbers That Matter Livestreams
In order to understand better how we got in this predicament, a brief history review is useful. Consumer demand for almost all goods collapsed due to the pandemic-induced shutdown, and this resulted in the collapse of the global supply chain. Shortly thereafter, the government stimulus checks started to arrive, and consumers proceeded to overspend on goods such as home furnishings, computer products and leisure equipment. Overall, total spending on goods boomed and total spending on services languished.
After a year or so, the U.S. economy gradually reopened, but consumer demand for "stay at home" types of products was beyond satiated. Since the second quarter of 2021, the amount of money spent on goods in the U.S. has actually been in decline when adjusted for inflation.
At the moment, consumer spending for goods is now back close to its long-term trend, but the trend in the data is aimed downward and there is mounting evidence that indicates this trend could overshoot to the downside. Consumer confidence levels have rebounded from the all-time lows they recorded this summer, but they remain subdued. In the third quarter of this year, the Fed aggressively began to raise interest rates in an effort to destroy demand.
As of yet, the rise in interest rates has not had a substantial impact on the macroeconomic data, and this includes the data on inflation. There are two reasons for this. First, a substantial percentage of consumer spending is for goods and services that are not financed, so rising interest rates will not immediately affect demand for these goods.
One exception to this is the auto sector. There was so much pent-up demand for autos that the rise in financing costs will take a little more time than usual before it starts to show up in the data. But make no mistake, that day is coming at an accelerating rate.
The second reason why we have yet to see an immediate effect on the economic data is there typically is a lag between the time the Fed starts raising rates and the time the full effect of these hikes is observed in the overall macroeconomic data. Keep in mind that the decision to raise rates was made because demand was too hot. It is only prudent for the Fed to try to cool demand gradually.
That implies there will be a lag. But it will happen. It may take another two or three or even four quarters to get there, but at some point in the near future, the employment data will turn negative and demand growth will revert back to its long-term trend.
It remains to be seen whether the trend in total demand will overshoot to the downside. If it turns negative for a sustained period of time, then the U.S. economy will officially enter into a recession. But recession or not, slower growth in spending is inevitable. Some of the early sectors that will be affected are the residential real estate and the residential construction sectors. It is quite possible that we are already past the peak in these sectors, though here again, pent up demand will affect the timing of these curves and also the impact these trends will have on demand for plastics products.
What does all of this mean for the plastics industry? It means the outlook for the coming year depends significantly on the end market sector in question. The segment with the largest imbalance between inventories and sales is motor vehicles and parts. There has been modest improvement in recent months, but this sector is by far the most out of balance of any of the major end markets. The processors that supply this sector will likely experience solid demand for a while longer.
End markets in which oversupply is already a significant risk include consumer nondurables, general merchandise consumer goods, home furnishings, electronics and appliances. The future trend in the data for consumer nondurables over the next few quarters will best be described as a reversion to the long-term mean as consumers rebalance their allocation between goods and services. Market demand for the more expensive items such as furnishings, electronics and appliances will be negatively impacted by the rising interest rates because many of these purchases tend to be financed.
To summarize, the global economy continues to struggle with the aftershocks of the pandemic, the ongoing uncertainty of the Ukraine/Russia conflict, and COVID zero-tolerance policy in China. These problems have resulted in high rates of inflation and destabilizing foreign exchange rates, particularly for currency pairs involving the U.S. dollar. It will likely take at least three or four quarters for these issues to return to a more stable point of equilibrium. Until then, the risks to the U.S. and global economies will remain elevated.
Source : https://www.plasticsnews.com/news/recession-or-not-expect-slower-growth-spending-inevitable
Edit : HANDLER
